Abstract
Background: Enasidenib (AG-221) and ivosidenib (AG-120) are oral, small-molecule inhibitors of mIDH2 and mIDH1proteins, respectively, both shown preclinically to reduce aberrant 2-HG levels and promote myeloid differentiation. As monotherapies, enasidenib and ivosidenib induce clinical responses in patients (pts) with m IDH relapsed/refractory AML. AZA monotherapy prolonged survival vs conventional care in older pts with newly diagnosed (ND) AML (10.4 vs 6.5 months, respectively; P= 0.101). AZA reduces DNA methylation by inhibiting DNA methyltransferases, and mIDH inhibitors indirectly reduce DNA methylation by suppressing 2-HG and restoring function to α-ketoglutarate-dependent TET family enzymes. In vitro, combinations of mIDH inhibitors + AZA showed synergistic effects on releasing differentiation block in m IDH leukemia models, providing a clinical rationale for combining these agents for treatment (Tx) of AML. Herein we report initial results of the phase 1b portion of an ongoing phase 1b/2 study of mIDH inhibitors + AZA combinations in pts with ND-AML (NCT02677922).
Methods: Eligible pts with m IDH ND-AML were aged ≥18 years and ineligible for intensive chemotherapy per investigator assessment. Pts with m IDH2 AML received enasidenib in dose-escalation cohorts of 100 or 200 mg QD and pts with m IDH1 AML received ivosidenib 500 mg QD, each in continuous 28-day cycles. All patients also received SC AZA 75 mg/m2/day x 7 days/cycle. Safety was assessed by Tx-emergent adverse event (TEAE) reporting. Efficacy was assessed per IWG criteria for AML; overall response rate (ORR) included complete remission (CR), CR with incomplete count recovery (CRi/CRp), partial remission (PR), and morphologic leukemia-free state (MLFS).
Results: At data cutoff (9 May 2017), 13 pts had received ≥1 dose of enasidenib 100 mg (n=3) or 200 mg (n=3) + AZA, or ivosidenib 500 mg (n=7) + AZA. Ten pts (77%) remained on-study: 2 pts in the enasidenib 100 mg + AZA arm, 2 pts in the enasidenib 200 mg + AZA arm, and 6 pts in the ivosidenib 500 mg + AZA arm.
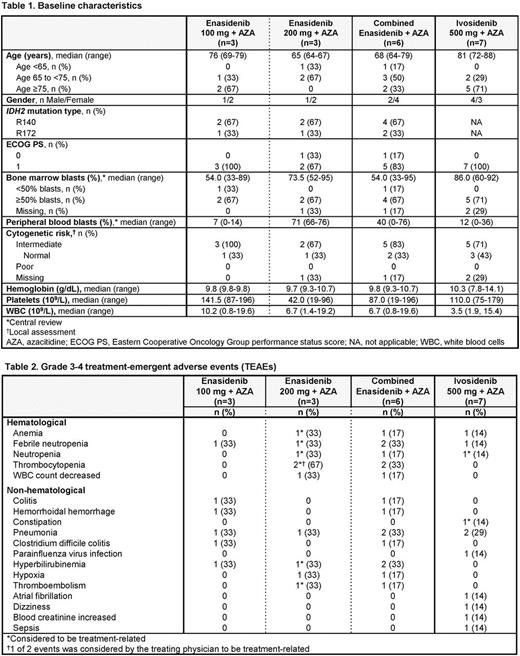
Enasidenib: Median age was 68 years (Table 1). Four pts had de novo AML and 2 pts had secondary AML (sAML). Median number of enasidenib Tx cycles overall was 6.5 (range 1-9). Two pts discontinued Tx due to progressive disease (PD), including 1 pt in the 200 mg arm who later died from a lung infection. The most common (>2 pts) TEAEs were hyperbilirubinemia and nausea (n=3 each). Tx-related TEAEs (any grade) in >1 enasidenib-treated pt were nausea and vomiting (n=2 each).Grade 3-4 TEAEs (any cause) are shown in Table 2. Three serious TEAEs in 1 pt were considered Tx-related: hyperbilirubinemia, febrile neutropenia, and a thromboembolic event in the leg. For enasidenib-treated pts, ORR was 3/6 at data cutoff. In the enasidenib 100 mg + AZA arm, the best responses on-study were 2 CRs; 1 pt had PD. In the enasidenib 200 mg + AZA arm, 1 pt achieved PR and 2 pts maintained stable disease (SD).
Ivosidenib: Median age was 81 years (Table 1). Six pts had de novo AML and 1 pt had sAML. Median number of ivosidenib Tx cycles was 4 (range 1-11).TEAEs (any grade) occurring in >2 pts were fatigue (n=6), nausea (5), and constipation (5). Tx-related TEAEs occurring in >1 pt were nausea (n=4) and fatigue (5). The only serious grade 3-4 TEAE occurring in >1 pt was pneumonia (n=2), from which 1 pt died on-study. Neither pneumonia event was considered Tx-related (Table 2). ORR was 3/5; all 3 responders attained CR and 2 pts maintained SD. The remaining 2 pts entered the study in March 2017 and had no response data available at data cutoff.
Conclusions: Enasidenib or ivosidenib + AZA combination regimens were generally well tolerated in pts with ND-AML, with 10 of the initial 13 pts remaining on-study at data cutoff, and only 2 discontinuations due to PD. The most common TEAEs with all regimens were grade 1 and 2 GI events and indirect bilirubin increases (likely due to off-target inhibition of UGT1A1 enzyme). Preliminary efficacy results with these combination regimens are encouraging, with 5 CRs and 1 PR on-study. Based on clinical activity and tolerability, the 100 mg enasidenib dose and 500 mg ivosidenib dose will move forward for further study in combination regimens. Evaluation of mIDH inhibitors + AZA continues in 2 currently enrolling randomized studies, including the expansion phase of the current study and the phase 3 AGILE study of ivosidenib + AZA (NCT03173248), to further assess the safety and clinical efficacy of these regimens.
DiNardo: Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Honoraria, Research Funding. Stein: Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Stemline: Consultancy. Fathi: Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Juno: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Agios: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Medimmune: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Montesinos: Celgene Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding. Odenike: Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Honoraria; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CTI/Baxalta: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kantarjian: Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding. Stone: Fuji Film: Consultancy; Ono: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Arog: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy; Sumitomo: Consultancy. Koralek: Agios Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Van Oostendorp: Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Gong: Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Gupta: Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Vyas: Celgene Corporation: Speakers Bureau; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal